
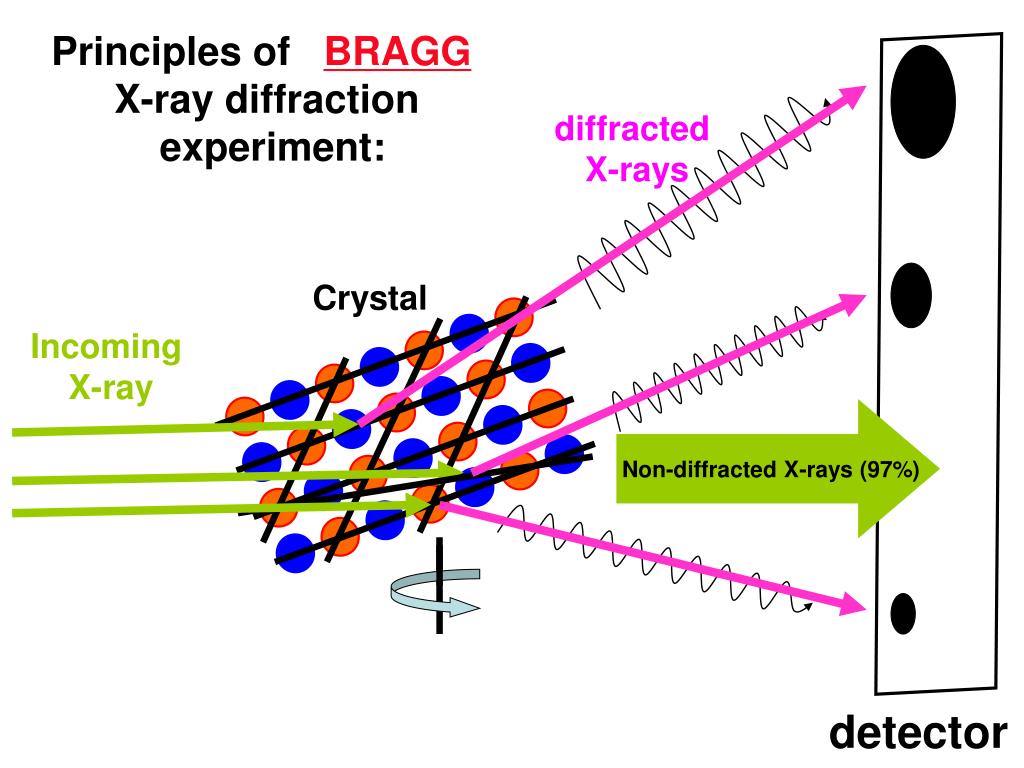
This review summarizes the scientific trends associated with the rapid development of the technique of X-ray diffraction over the past five years pertaining to the fields of pharmaceuticals, forensic science, geological applications, microelectronics, and glass manufacturing, as well as in corrosion analysis. Consequently, the X-ray diffraction pattern is the fingerprint of periodic atomic arrangements in a given material. The peak intensities are determined by the distribution of atoms within the lattice. X-ray Diffraction Studies: The X-ray diffraction patterns for the silk films and silk fibers were recorded using Righaku Denki. x-ray diffraction Technique utilized to study atomic structure of crystalline substances by noting the patterns produced by x-rays shot through the crystal.
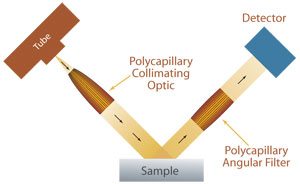
It provides information on structures, phases, preferred crystal orientations (texture), and other structural parameters, such as average grain size, crystallinity, strain, and crystal defects. The scattering of x-rays by crystal atoms, producing a diffraction pattern that yields information about the structure of the crystal. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a powerful nondestructive technique for characterizing crystalline materials. X-ray diffraction peaks are produced by constructive interference of a monochromatic beam of X-rays scattered at specific angles from each set of lattice planes in a sample. X-ray diffraction A method for studying microscopic crystal form and structure. x-ray diffraction synonyms, x-ray diffraction pronunciation, x-ray diffraction translation, English dictionary definition of x-ray diffraction. X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a powerful nondestructive technique for characterizing crystalline materials.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
